Tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos ^2 (x) sin ^2 (x) = 2 cos ^2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin ^2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1Using following trigonometric identities Sinx^2Cosx^2==1 Sinx/Cosx==Tanx Cscx==1/Si Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careersI am trying to express this problem in terms of sin/cos and simplify I couldn't figure out where to go, I tried as best I could I know the answer is 1 but I am more interested to know how to do this problem $$ \tan^2x \sec^2x $$ $$ (\sin x / \cos x)^2 (x / \cos x)^2 $$
Solved Prove The Identity 2 Tan X Sin 2x 1 Tan2x Wr Chegg Com
Tan 2x in terms of sin x
Tan 2x in terms of sin x-Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepTrigonometric functions sin x, cos x, tan x The trigonometeric functions, the sine function (sin) and cosine function (cos) are obtained for a = 1 Hyperbolic functions cosh x, sinh x, tanh x



Prove That Sin3x Sinx Cosx Cos3x Tan2x Brainly In
In this video, I show how with a right angled triangle with hypotenuse 1, sides (a) and (b), and using Pythagoras' Theorem, thatcos(x) = 1 / sqrt( 1 tan^2Tan2x Formula Sin 2x, Cos 2x, Tan 2x is the trigonometric formulas which are called as double angle formulas because they have double angles in their trigonometric functions Let's understand it by practicing it through solved example Introduction to Tan double angle formula1Rewrite cos(x−3π/4) in terms of sin(x) and cos(x) 2If tan(x)=7/8 (in QuadrantI), find cos(2x)= 3 Simplify without a calculator 2cos^2(15 degree )1 4If sin(π/12)=1/2√ (A−√B), then, by using a halfangle formula, find A= B= 5Use half angle formulas or formula for reducing powers to fill in the blanks in the identity below
INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS 23 Therefore, tan(cos–1x) = 1–cos θ 21– tanθ = cosθ x x = Hence 2 –1 8 1– 8 17 15 tan cos = 17 8 8 17 = Example 11 Find the value of –1 –5Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreA half turn, or 180°, or π radian is the period of tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x) and cot(x) = cos(x) / sin(x), as can be seen from these definitions and the period of the defining trigonometric functions Therefore, shifting the arguments of tan(x) and cot(x) by
We also know the Pythagorean Identity sin 2 (x) cos 2 (x) = 1 Can you use this to write an expression for cos 2 (x) in terms of sin 2 (x)?Apr 05, 21 · Simplify and write the trigonometric expression in terms of sine and cosine tan^2 xsec^2 x= mathematics Write the following trigonometric expression in terms of sine and cosine, and then simplify sin^2 x (1 cot^2 x) math Rewrite the expression as an algebraic expresion in x tan(sinHow does that, then, help you write an expression for cos(x) in terms of sin 2 (x)?



F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2



Powers Of Trigonometric Functions
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorSimplify the trigonometric expression below by writing the simplified form in terms of sin x Enclose arguments of Answered by a verified Tutor We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website (sin 2x6e^3x)dx x^2(2x^3)^3 dx sec(x)tan (x)May 12, 21 · Misc 15 sin(tan−1 x), 𝑥 < 1 is equal to (A) 𝑥/√(1 − 𝑥2) (B) 1/√(1 − 𝑥2) 1/√(1 𝑥2) (D) 𝑥/√(1 𝑥2) Let a = tan−1 x tan a = x We need to find sin a For this first we calculate sec a and cos a We know that sec2 a = 1 tan2 a sec a = √(1𝑡𝑎𝑛2 a) We convert t



5 5 Multiple Angle And Product Sum Formulas Find All Solutions In Ppt Download



Prove That Sin3x Sinx Cosx Cos3x Tan2x Brainly In
Nov 21, 19 · sin^2(x) cos^2(x) = 1, so combining these we get the equation cos(2x) = 2cos^2(x) 1 Now we can rearrange this to give cos^2(x) = (1cos(2x))/2 So we have an equation that gives cos^2(x) in a nicer form which we can easily integrate using the reverse chain rule This eventually gives us an answer of x/2 sin(2x)/4 c Integral of sin^2xDec 23, 19 · Misc 31 Evaluate the definite integral ∫_0^(𝜋/2) 〖sin2𝑥 tan^(−1)(sin𝑥 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 ∫_0^(𝜋/2) 〖sin2𝑥 tan^(−1)(sin𝑥 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_0^(𝜋/2) 〖2 sin𝑥 cos𝑥 tan^(−1)(sin𝑥 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 Let sinSave 1 sin factor & use sin^2(x)=1cos^2(x) to express remaining in terms of cos Then sub u=cosx When evaluating antiderivative of sin^m(x)*cos^n(x)dx, if power of both SIN and COS are EVEN


Differentiate The Following From First Principles I Tan 2 X Ii Tan 2x 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Inttanx Tan2x Tan3x Dx Is Equal To
This is a quadratic in tan(x) which we can solve in terms of tan(2x) (pretend tan(2x) is a constant and write tan(x) as u if it makes things clearer ie tan(2x)*(1u^2) 2u = 0 and use the quadratic equation on this)Math\sin^2x\cos^2x=1/math math\implies\dfrac{\sin^2x}{\cos^2x}\dfrac{\cos^2x}{\cos^2x}=\dfrac{1}{\cos^2x}/math math\implies\left(\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x21) sec 4 x tan 4 x = sec 2 x tan 2 x 21) Graph the expression on each side of the equals symbol to determine whether the equation might be an identity 22) sin θ 1 cos θ cot θ = tan θ 22) Use Identities to find the exact value 23) cos 75° 23) 24) cos π 12 24)



Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified
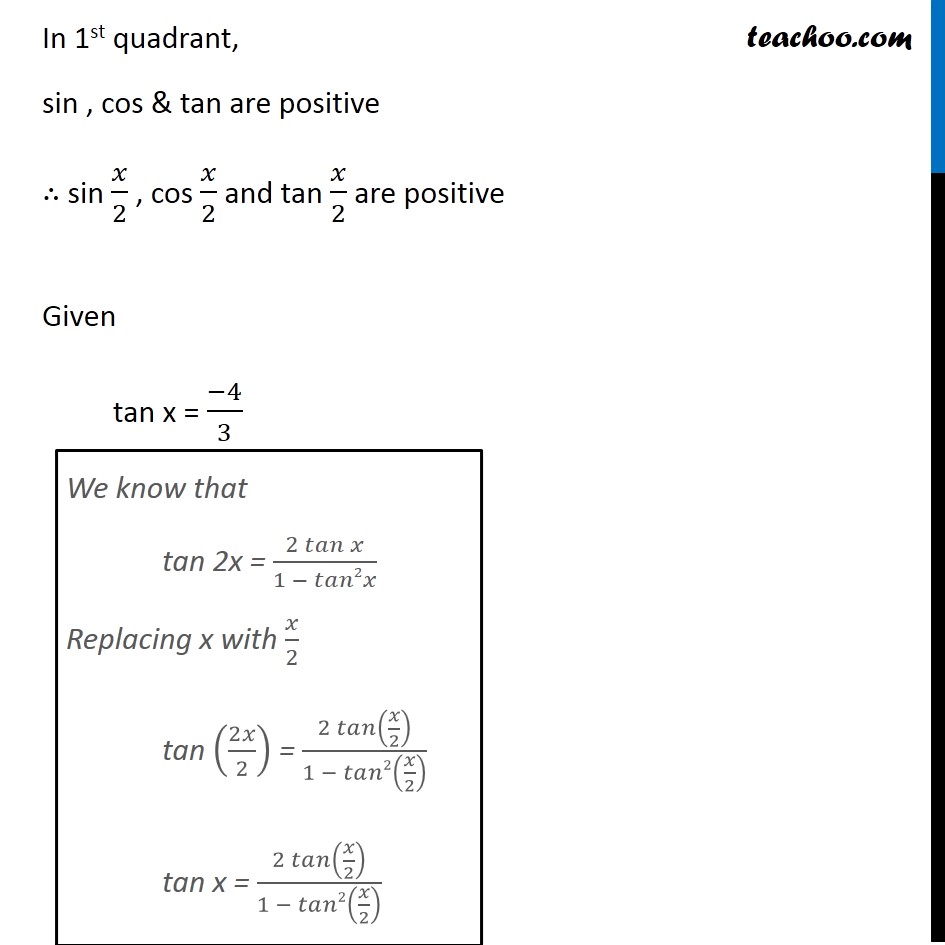


Misc 8 Tan X 4 3 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 And Tan X 2
May 08, 12 · The standard way would be to simply write the tangent function as the ratio of sine and cosine, and then use the relationship between those two to rewrite, say, itex\text{sin}(\frac{\pi}{2}x)/itex in terms of itex\text{cos}(x)/itexGet an answer for 'Prove that tan^2x/(1tan^2x) = sin^2x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesQ Choose a good way to start solving this equation tanx sin 2 x = 2 tanx



Math34 Trigonometric Formulas


What Is Tan 2 X Equal To
Sep 25, 09 · Well tan2x=Sin2x/Cos2x then Sin2x= Tan2x*Cos2x but note that Cos^2 (2x)=1/Sec^2 (2x) using sec^2 (2x)=1 tan^2 (2x) we then get Sin2x=Tan2x/Sqrt (1tan^2 (2x)) this is all ok but sin2x=2sinxcosx so you need to do the same for cos2x and find cosx in terms of tan2x thus replace it into the expression above I hope this helpsGeometrically speaking, is the slope of the tangent line of at As an example, if , then and then we can compute The derivative is a powerful tool with many applications For example, it is used to find local/global extrema, find inflection points, solve optimization problems and describe the motion of objectsFree trigonometric simplification calculator Simplify trigonometric expressions to their simplest form stepbystep



If Sin X 5 3 And 0 Lt X Lt P 2 Find The Value Of Sin 2x Cos 2x Tan 2x Brainly In



Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Tan X 1 2 And X Terminates In Quadrant Iii Helpyout
Rewrite tan^2x sin^2x in terms of cosine without power greater than one Rewrite cot^2〖x/4〗 in terms of cosine without power greater than one Assume that x is in QI 34,817 results, page 11Q Simplify (secx1)(secx1) Hint you will need to FOIL first answer choices tan 2 xSo how can we do that?
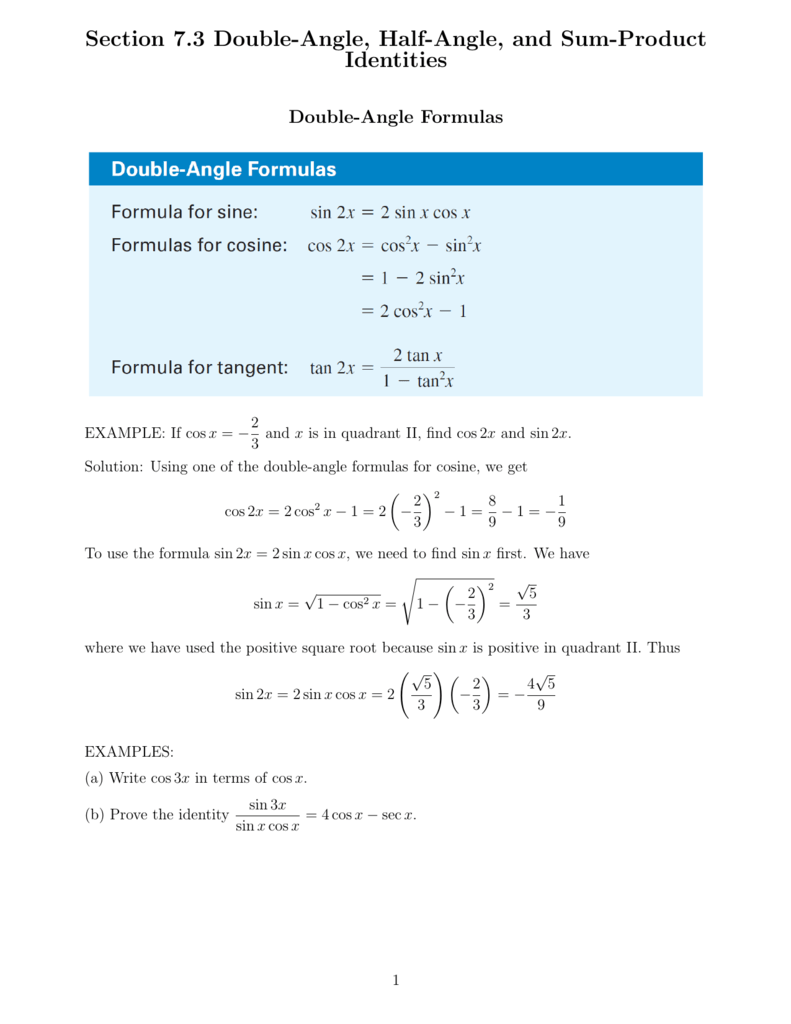


Section 7 3 Double Angle Half Angle And Sum



View Question Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x From The Given Information Tan X 1 2 Cos X 0
Prove the identity 2 tan(x) sin(2x) 1 tan2x) Write the more complicated side of the equation in terms of sin(x) and cos(x) Simplify the complex fraction 2 cos(x) 2 tan(x) 1 tan2(x) 1 cos2x) cos2(x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x) 1 sin?(x) cos(x) 2 II cos2(x) sin2(x) 2 sin(x) cos(x) 11 = Consider the following cos(2a) = 1 tan?(Q) 1 tan(a) Prove the identity 1 1 tan2@) 1 tan2(a) sinSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreSuppose our integrand is a rational function of sin(x) and cos(x) After the substitution z = tan(x / 2) we obtain an integrand that is a rational function of z, which can then be evaluated by partial fractions Theorem If z = tan(x / 2), then ,, and and any rational function of xdx becomes a rational function of zdz Proof Example



Solved Prove The Identity 2 Tan X Sin 2x 1 Tan2x Wr Chegg Com



Expressing Sin X And Cos X In Terms Of T Tan X 2 Youtube
Three examples are that (1) any trigonometric expression can be converted to an expression in terms of only sin and cos, (2) expressions involving exp(x) can be converted to their hyperbolic forms, and (3) a trigonometric function with an argument of the form q A First rewrite the left hand side 1 tan^2x, in terms of sin x and cos x b Next, add the two terms in the expression you got in part (a) c Then, use the Pythagorean identity sin^2xcos^x=1 to simplify what you got in part b d Last rewrite what you have in part c in terms of sec x aGraph f(x)= cos(x) on the interval 0,2piSimplify (sin(x))/(tan(x)) Rewrite in terms of sines and cosines Multiply by the reciprocal of the fraction to divide by Write as a fraction with denominator Cancel the common factor of
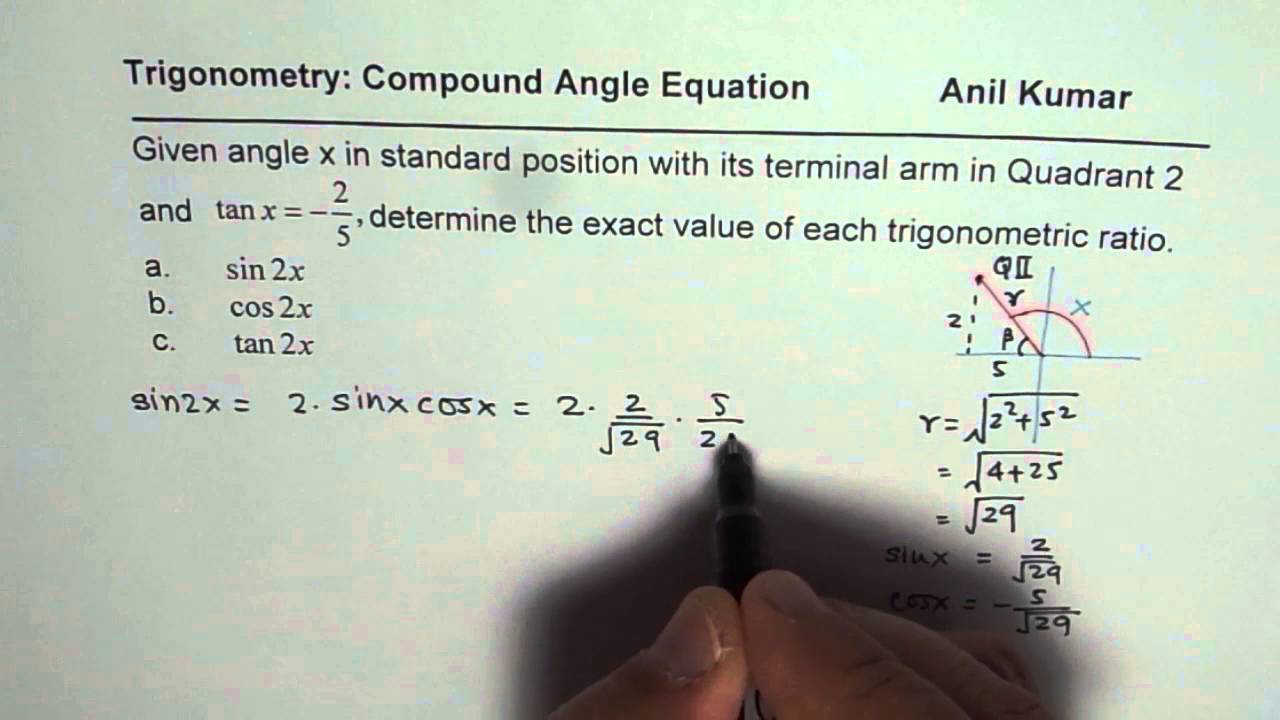


Calculate Sin2x Cos2x And Tan2x For Given Tanx In Quadrant 2 Youtube


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora
π, where q is a rational, can in some cases be converted toSin(2A) = sin(A)cos(A) cos(A)sin(A) = 2sin(A)cos(A) It is common to see two other forms expressing cos(2A) in terms of the sine and cosine of the single angle A Recall the square identity sin 2 (x) cos 2 (x) = 1 from Sections 14 and 23 This identity can be rewritten asWrite {eq}\tan x {/eq} in terms of {eq}\sec x {/eq} Trigonometric Identities As we know the most basic trigonometric expressions are constituted by the sine and by its most similar function
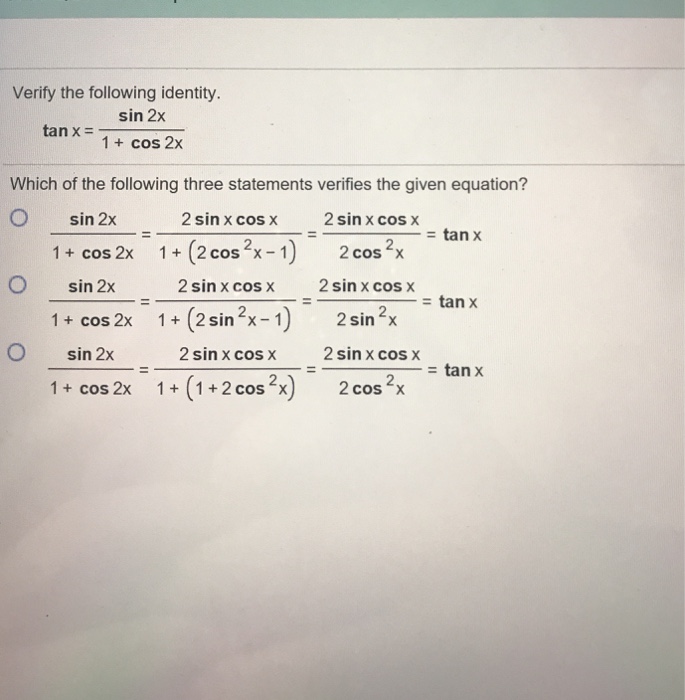


Solved Verify The Following Identity Tan X Sin2x 1 Co Chegg Com



Integrate Tan 2x By Parts
May 16, 16 · tan 2x = ((2sin x)/(1 2sin^2 x))sqrt(1 sin ^2 x) sin 2x = (sin 2x)/(cos 2x) Applying the 3 trig identities sin 2x = 2sin xcos x , and cos 2x = (1 2sin^2 xGet an answer for 'Prove tan^2x sin^2x = tan^2x sin^2x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesIf you plug this into the earlier formula for tan(x), do you get one of the answer choices?


Prove That Cos2x Cos 2x Sin 2x 2cos 2x 1 1 2sin 2x 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Solve For X Y And Z If Tan 2x Cot 2x 2sin 2y And Sin 2y Cos 2z 1 Askiitians
Aug 18, 01 · If units of degrees are intended, the degree sign must be explicitly shown (eg, sin x°, cos x°, etc) Using this standard notation, the argument x for the trigonometric functions satisfies the relationship x = (180x/π)°, so that, for example, sin π = sin 180° when we take x = π In this way, the degree symbol can be regarded as aEven though each trigonometry function is perfectly wonderful, being able to express each trig function in terms of one of the other five trig functions is frequently to your advantage For example, you may have some sine terms in an expression that you want to express in terms of tangent, so that all the functionsAfter doing so, the first of these formulae becomes sin(x x) = sin x cos x cos x sin x so that sin2x = 2 sin x cos x And this is how our first doubleangle formula, so called because we are doubling the angle (as in 2A) Practice Example for Sin 2x If we want to solve the following equation We will follow the following steps Step 1



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia


What Is The Identity Tan 2x Equal To In Terms Of Sinx And Cosx Quora
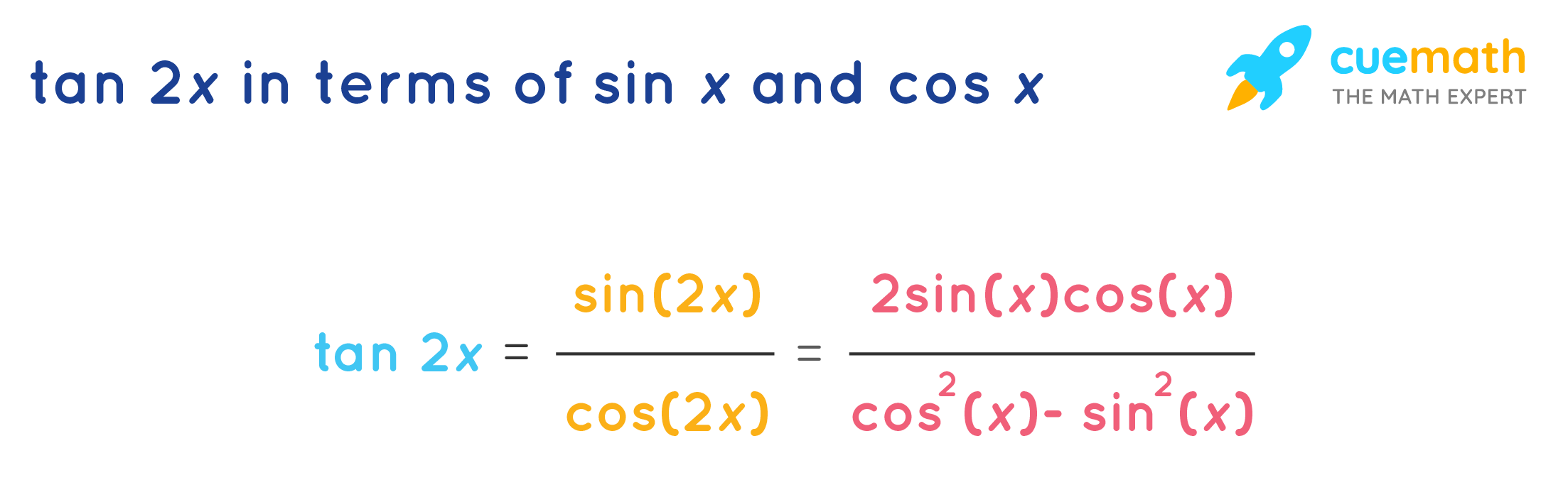


Tan 2x Formula Learn Formula For Calculating The Double Angle Tan 2x



Dana Harrington I Need Some Math Help From My Mtbos Iteachmath Precalcchat Friends I Am Stumped On How To Explain This We See All 6 Answers When We Graph We



If Sin X 1 5 And X Is In Quadrant I Find The Exact Values Of The Expressions Without Solving For X Wyzant Ask An Expert
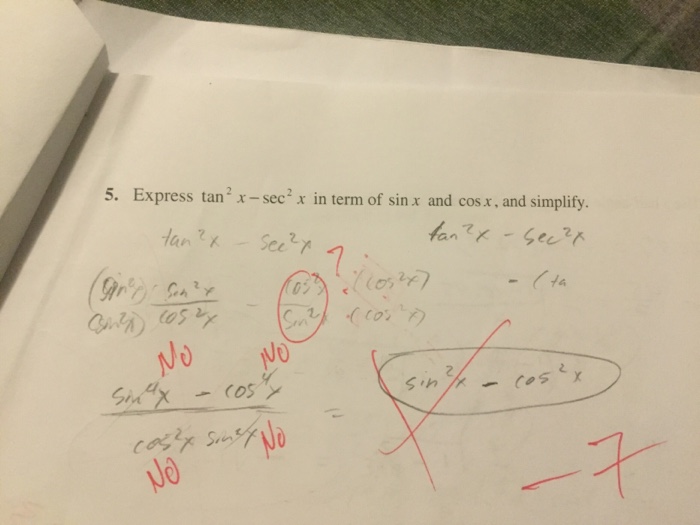


Solved Express Tan 2 X Sec 2 X In Term Of Sin X And Cos Chegg Com


Solved A First Rewrite The Left Hand Side 1 Tan 2x In Terms Of Sin X And Cos X B Next Add The Two Terms In The Expression You Got In Part



The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit
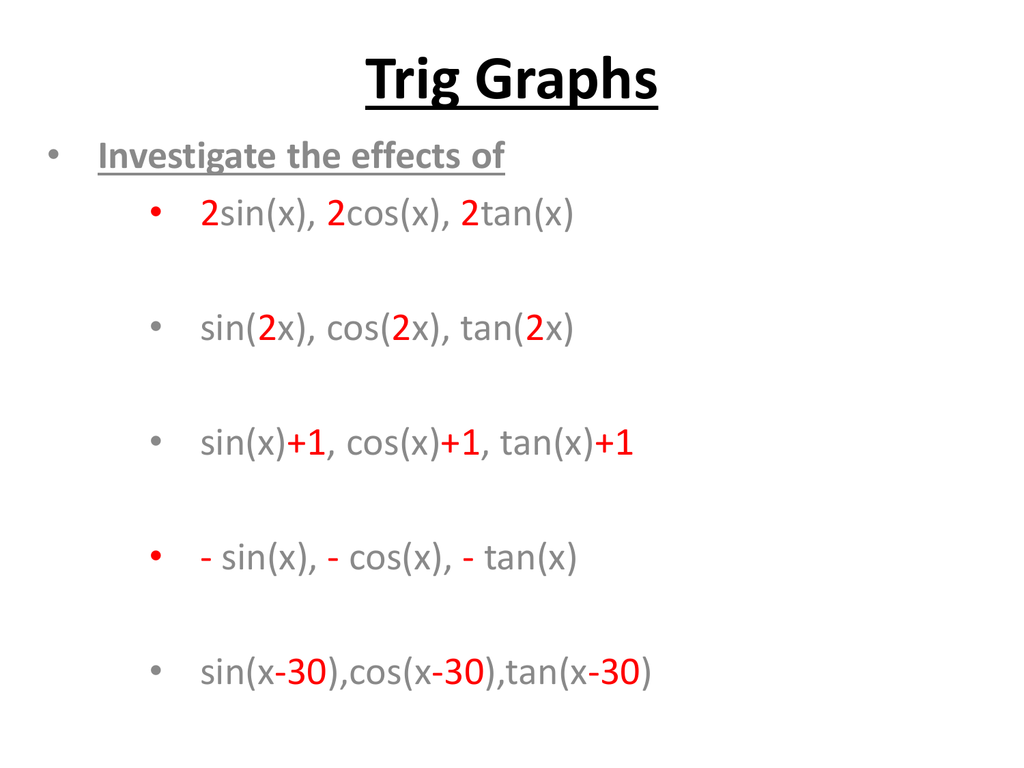


Trig 2 Caldervale High School



How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic



Section 7 3 Double Angle And Half Angle Formulas Flashcards Quizlet
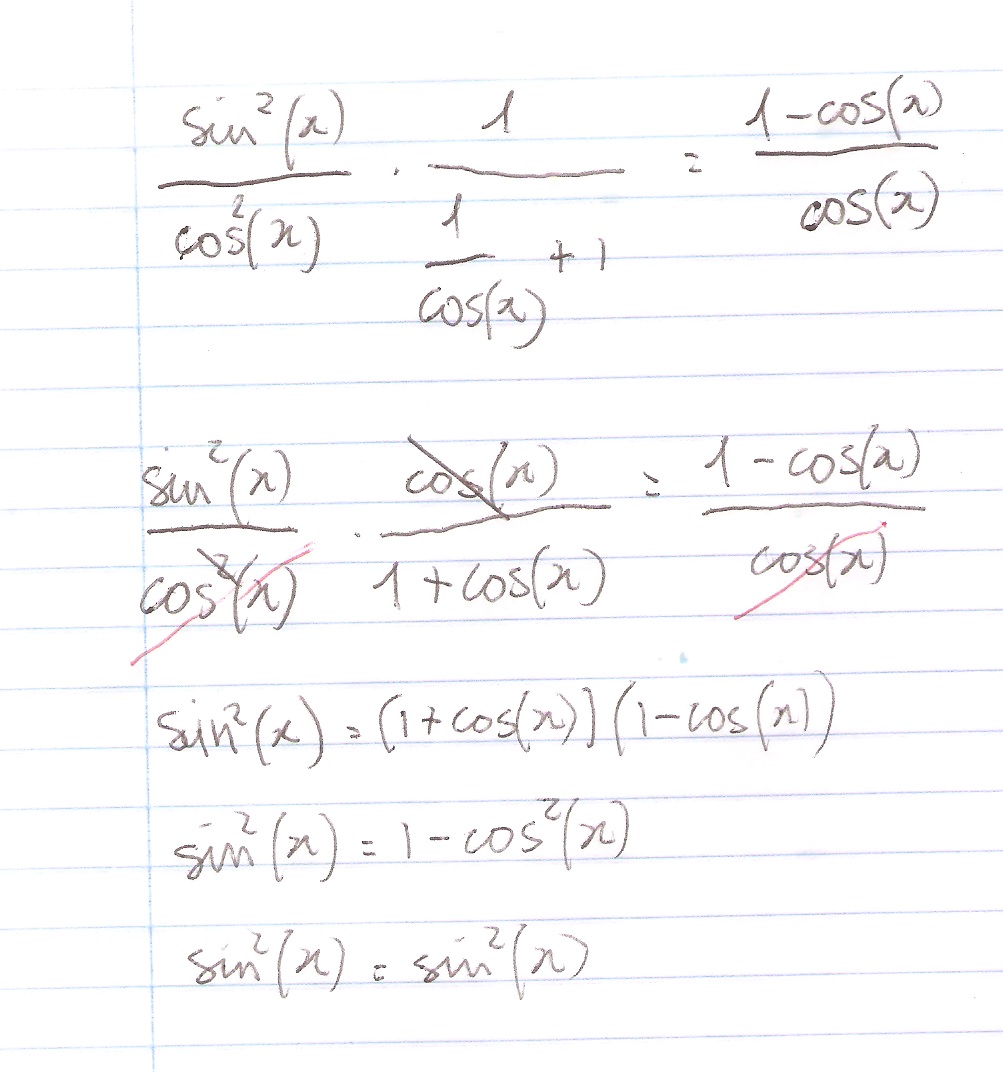


How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic



Tan 2x Cot 2x 2
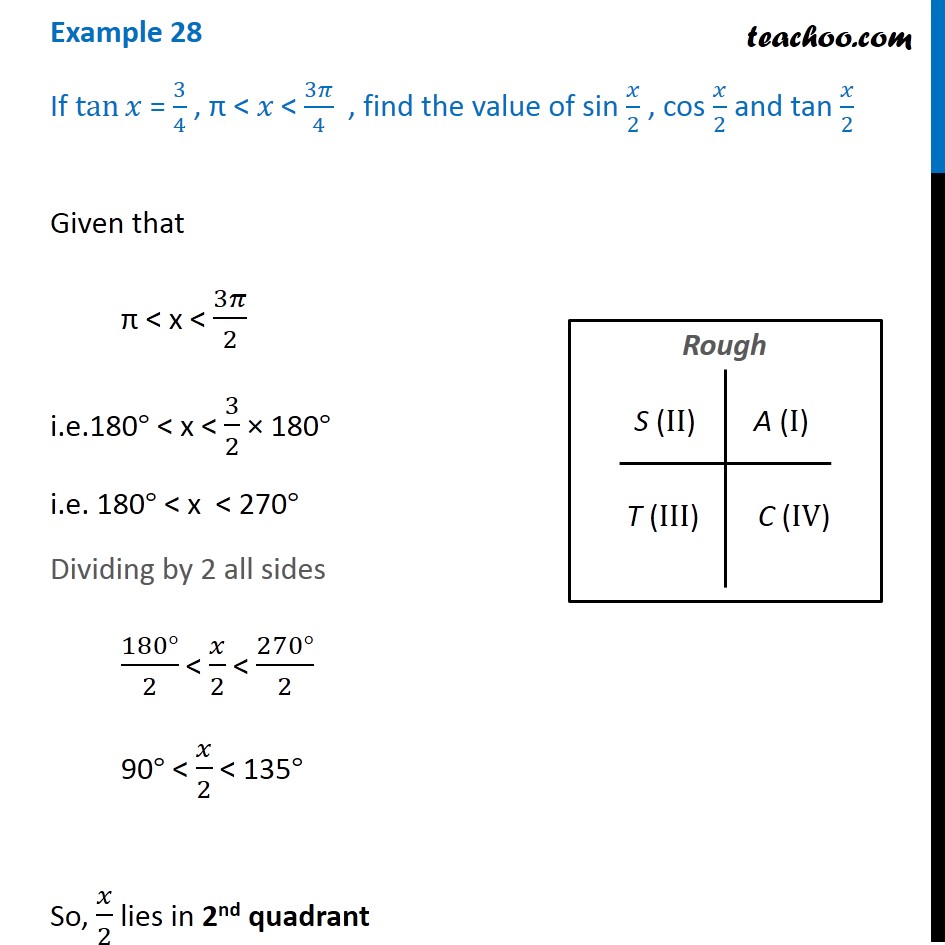


Example 28 If Tan X 3 4 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 Tan X 2



Frac Cos Xcos X Sin X Frac Cos Xcos X Sin X Tan 2x Gauthmath



Math34 Trigonometric Formulas



Solved Problem 4 Using The Sin And Cos Addition Formulas Chegg Com



2sinxcosx Identity Gamers Smart
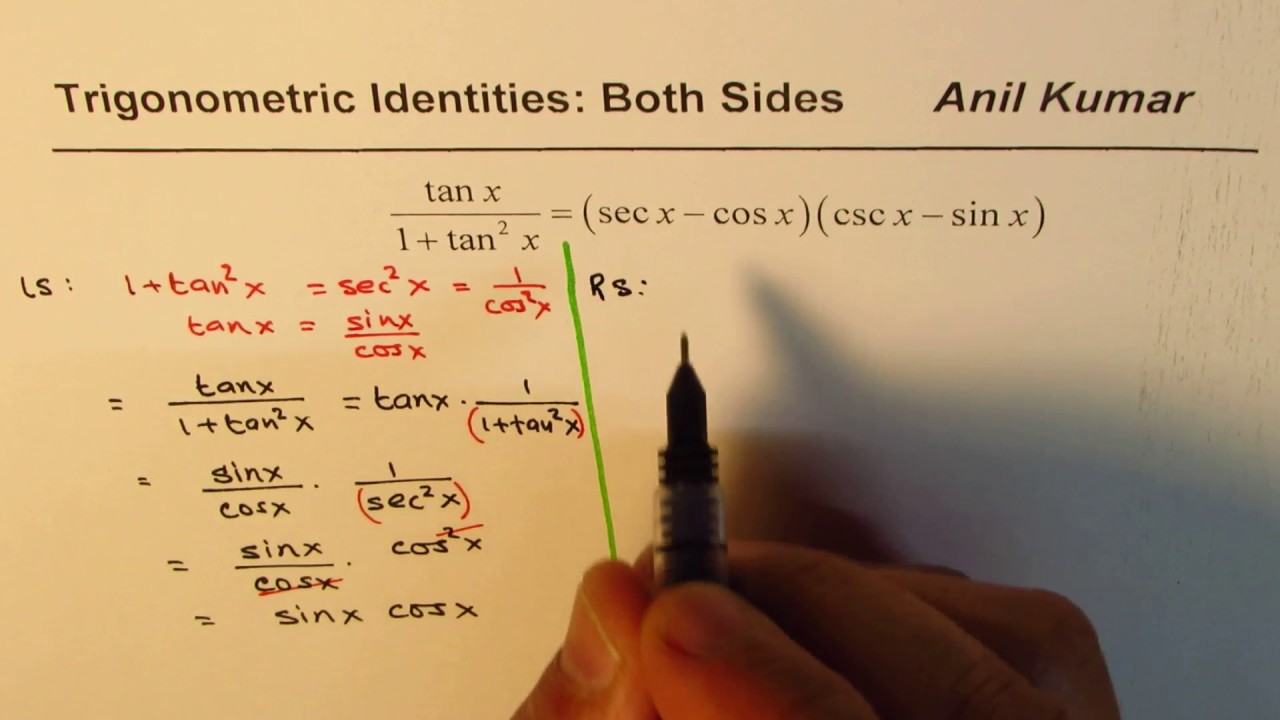


Trig Identity Tan X 1 Tan 2 X Sec X Cos X Csc X Sin X Proved From Both Sides Youtube


How To Write Sin X In Terms Of Tan X Quora



Solved Verify That The Equation Is An Identity 1 Tan X Chegg Com



Ex 3 3 19 Prove Sin X Sin 3x Cos X Cos 3x Tan 2x



Solved Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x From The Given Chegg Com


Is Tan 2x Equal To Tan X 2
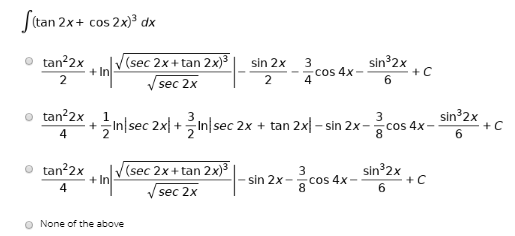


Answered Stan 2x Cos 2x Dx Tan 2x 2 V Sec 2x Bartleby
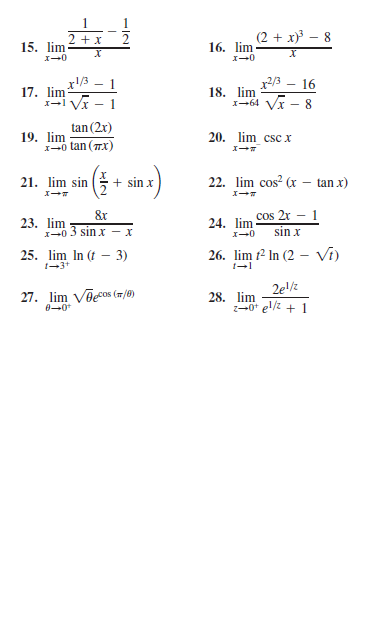


Answered X 2 X 8 15 Lim 16 Lim X2 3 Bartleby



Solved Section 7 3 Double Angle Half Angle And Product Chegg Com



Answered Power Reducing Formulas Cos 2x 1 Cos Bartleby


Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像


Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question



Lesson 4 5 Double Angle Formulas


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia


Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions


Solved A First Rewrite The Left Hand Side 1 Tan 2x In Terms Of Sin X And Cos X B Next Add The Two Terms In The Expression You Got In Part



Prove That Cot 2x Tan 2x 4cot2xcosec2x Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com


Trigonometric Functions Of Double Angles Expressed By The Tangent Function Trigonometric Functions Expressed By The Tangent Of The Half Angle Trigonometric Identities Examples



Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Sinx 5 13 And X Terminates In Quadrant I Ala Sin 2x U H Cos Brainly Com
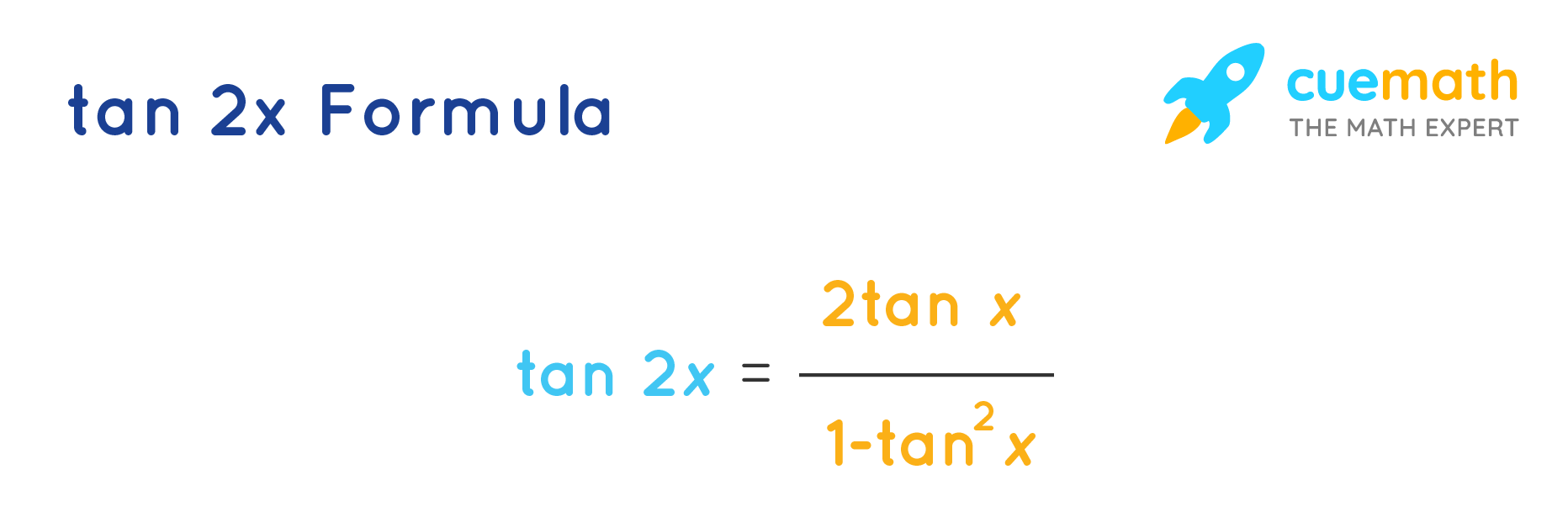


Tan 2x Formula Learn Formula For Calculating The Double Angle Tan 2x
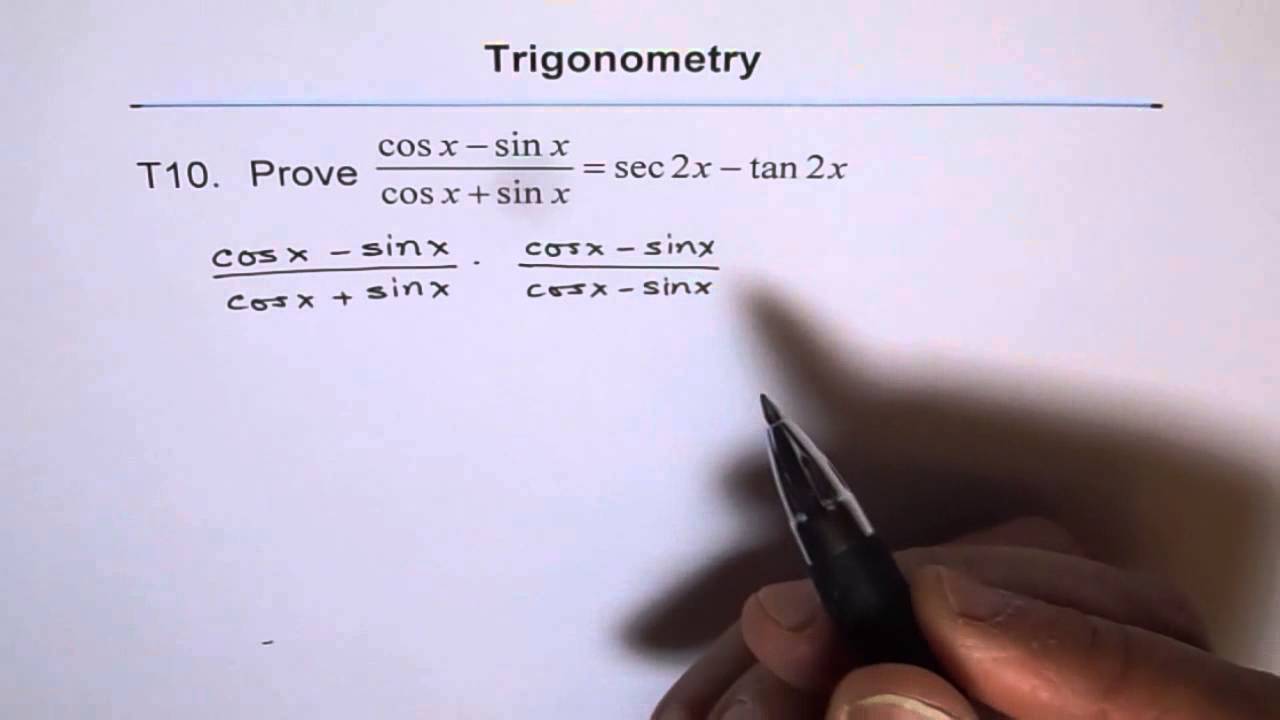


Trig Identity Sec2x Minus Tan2x T10 Youtube



Derivative Rules For Trigonometric Functions



How To Write Double Angle Formula Sin 2x In Terms Of Tan X Youtube


Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x
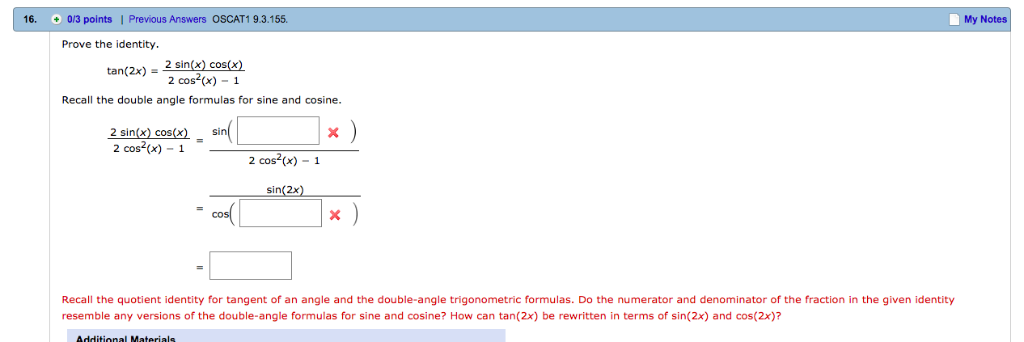


Solved 16 0 3 Points Previous Answers Oscat1 9 3 155 Chegg Com



How Do You Integrate 1 Sin2x Tan2x With Respect To X Maths Integrals Meritnation Com
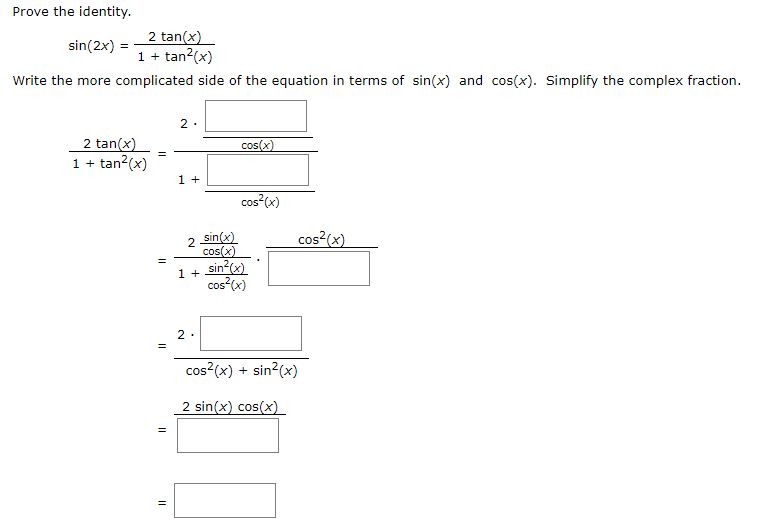


Solved Prove The Identity 2 Tan X Sin 2x 1 Tan2x Wr Chegg Com



Lesson 24 Double Angle Half Angle Identities Ppt Video Online Download



If Sin X Sqrt 5 3 And 0 Lt X Lt Pi 2 Find The Valu



Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia



Double Angle Properties Rules Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic
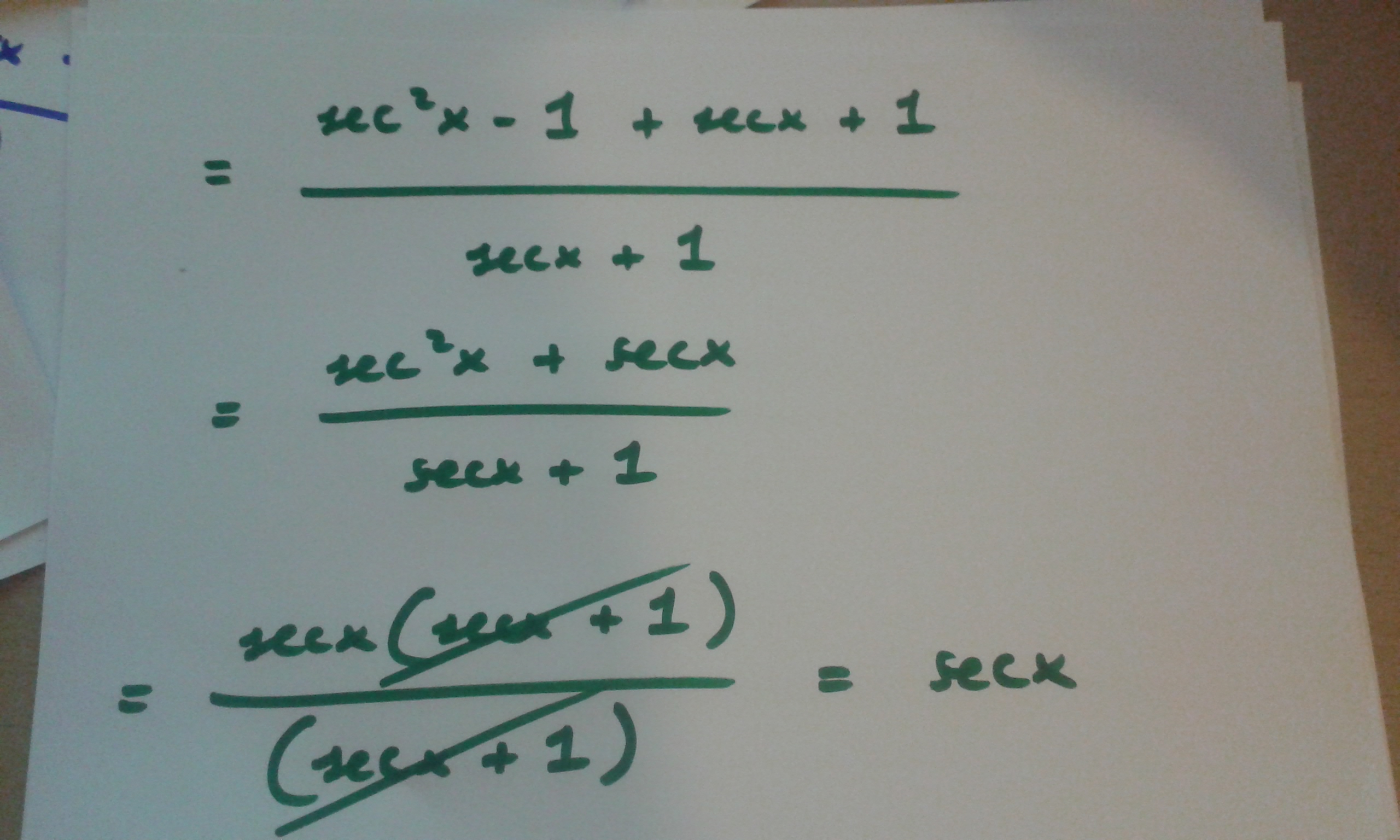


How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
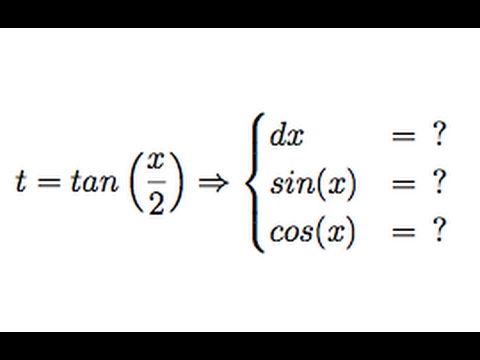


T Tan X 2 Weierstrass Substitution Youtube


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora


Derivatives Of Sin X Cos X Tan X Eˣ Ln X Video Khan Academy
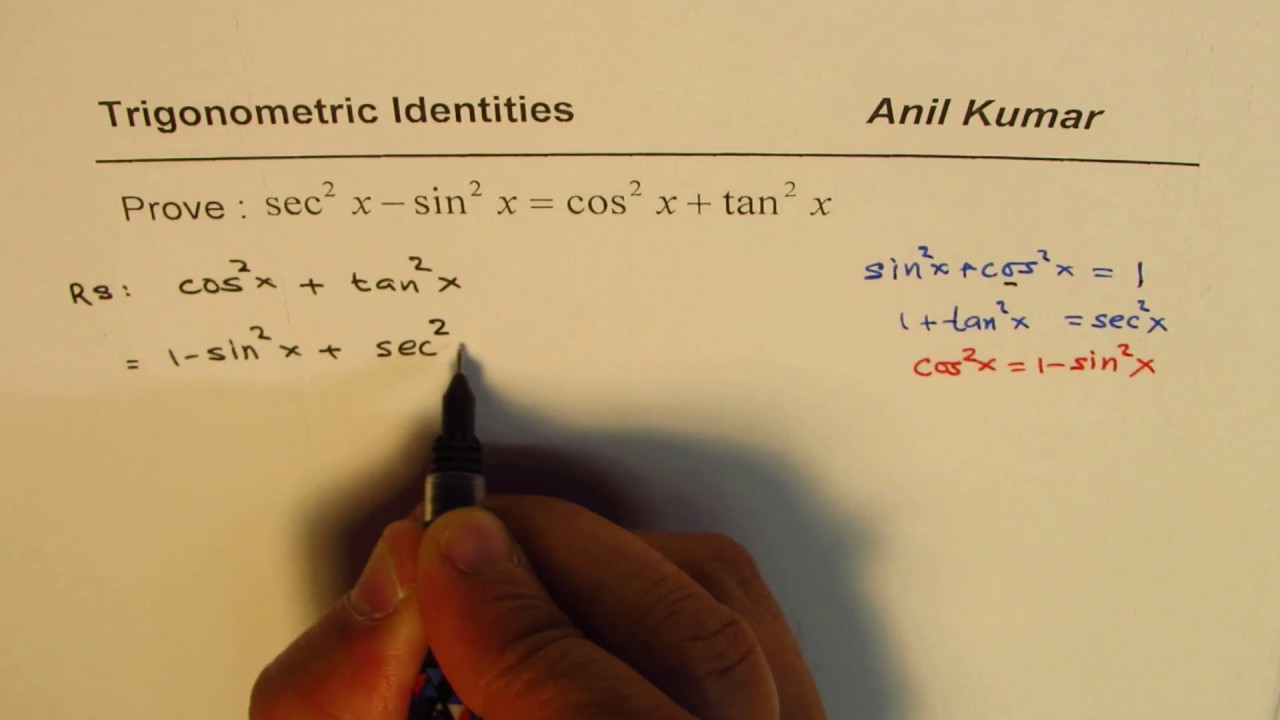


Trigonometric Identity With Pythagorens Sec 2x Sin 2x Cos 2x Tan 2x Youtube



Rewrite Sin 2x Tan 2x In Terms Of The First Power Of Cosine Using The Power Reducing Formula Study Com



Exercise 7 3 Integrals Of The Functions In Exercises 1 To 22 2 Sin 3x Cos 4x 3 Cos 2x Cos 4x Cos 6x 5 Sin X Cos 6 Sin X Sin 2x
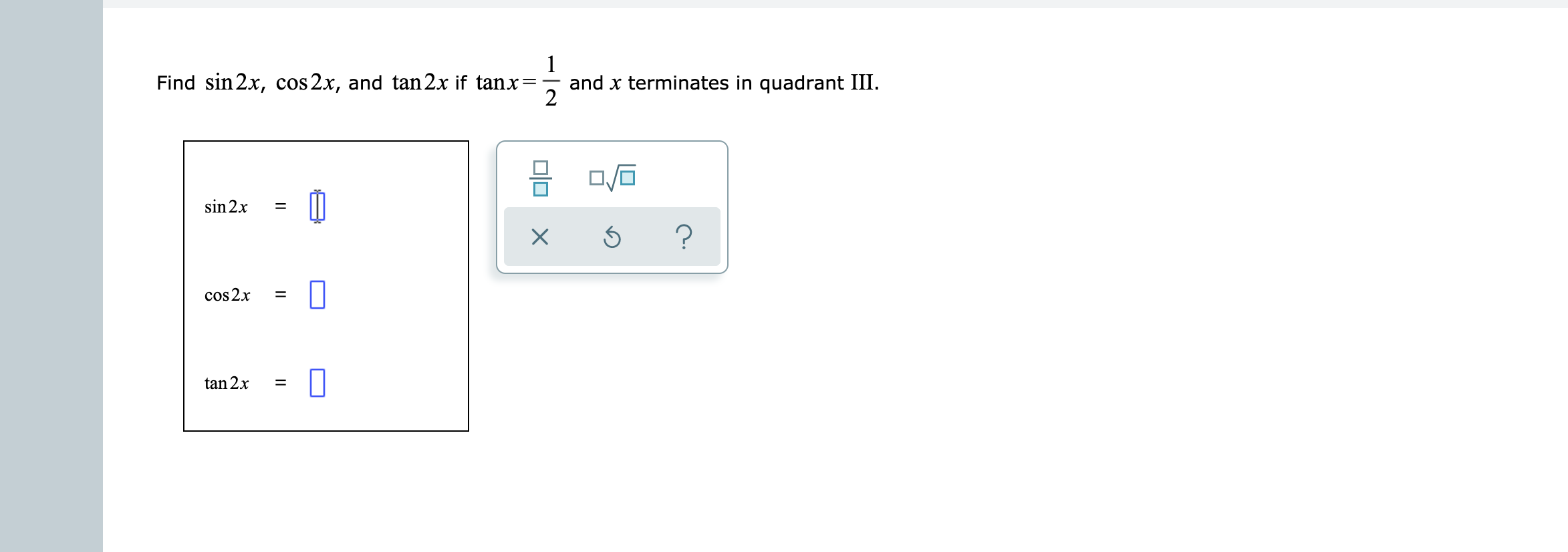


Answered 1 Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Bartleby
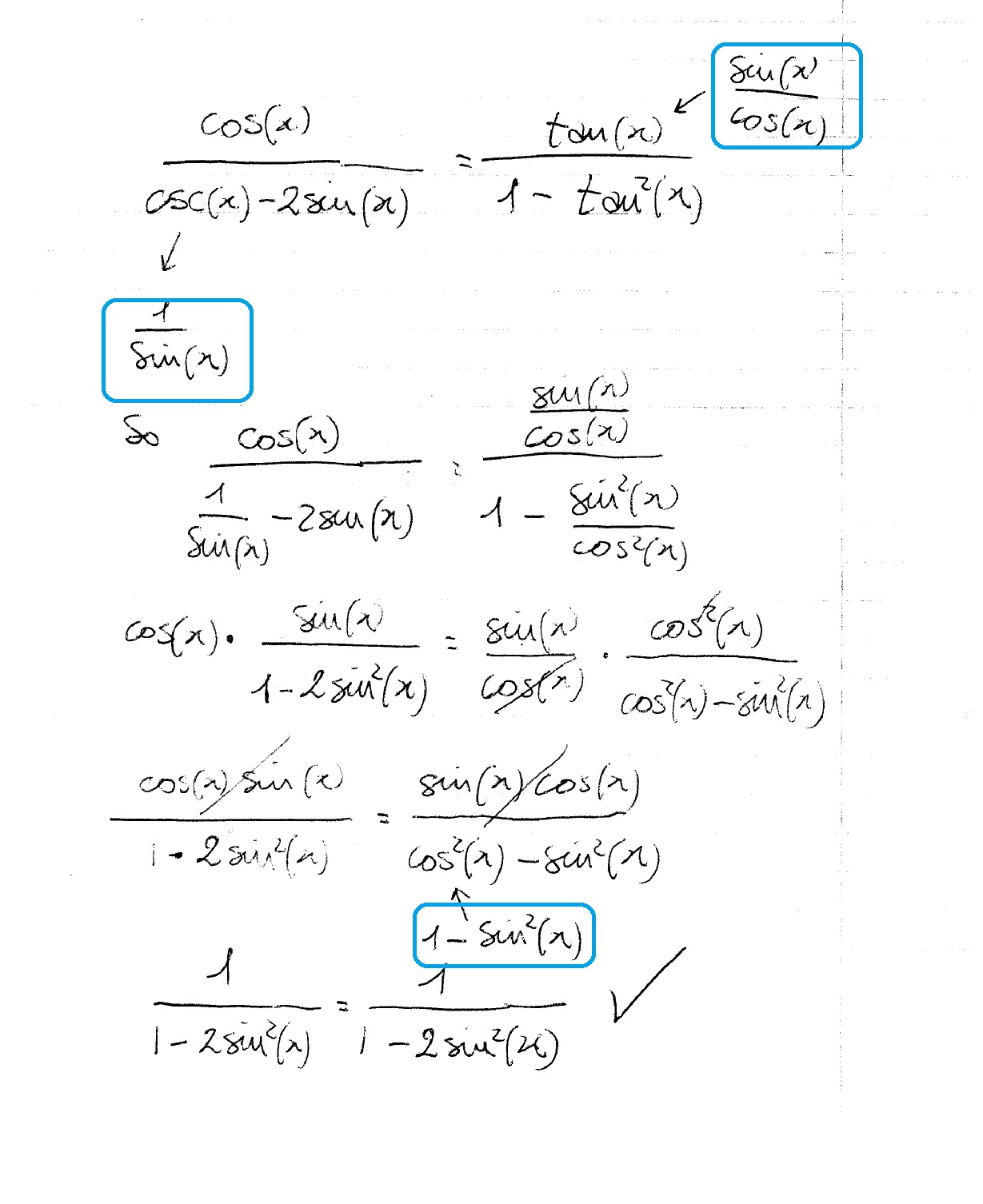


How Do You Prove Cosx Cscx 2sinx Tanx 1 Tan 2x Socratic



Ch 6 Review Assignment Key



Qprove That Tan X 2 Tan 2x 4 Tan 4x 8 Cot 8x Cot X Mathematics Topperlearning Com Blpusg55
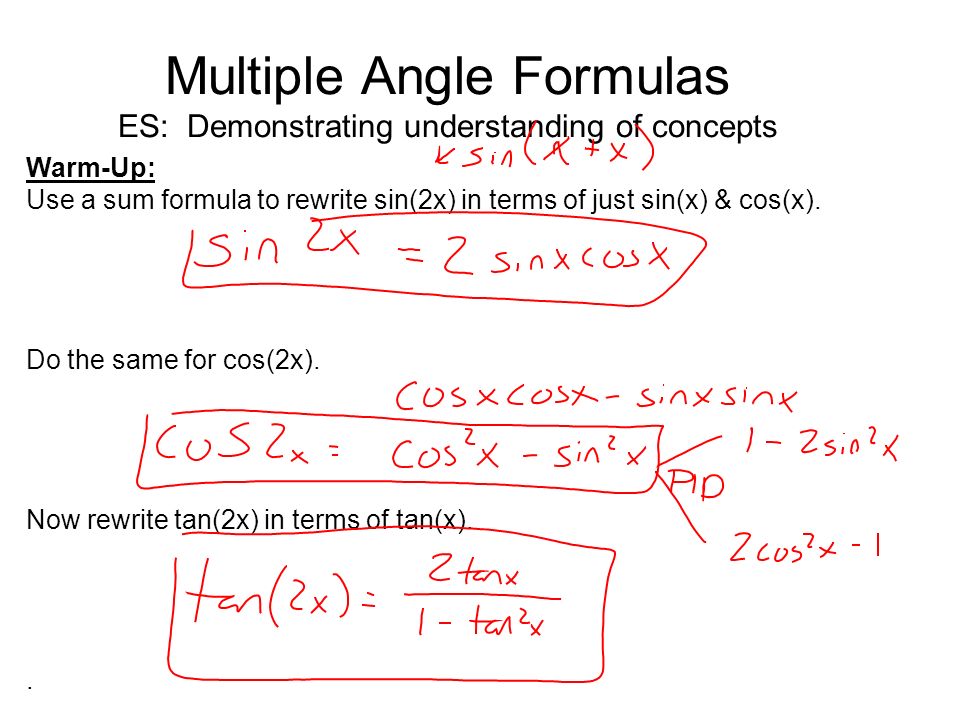


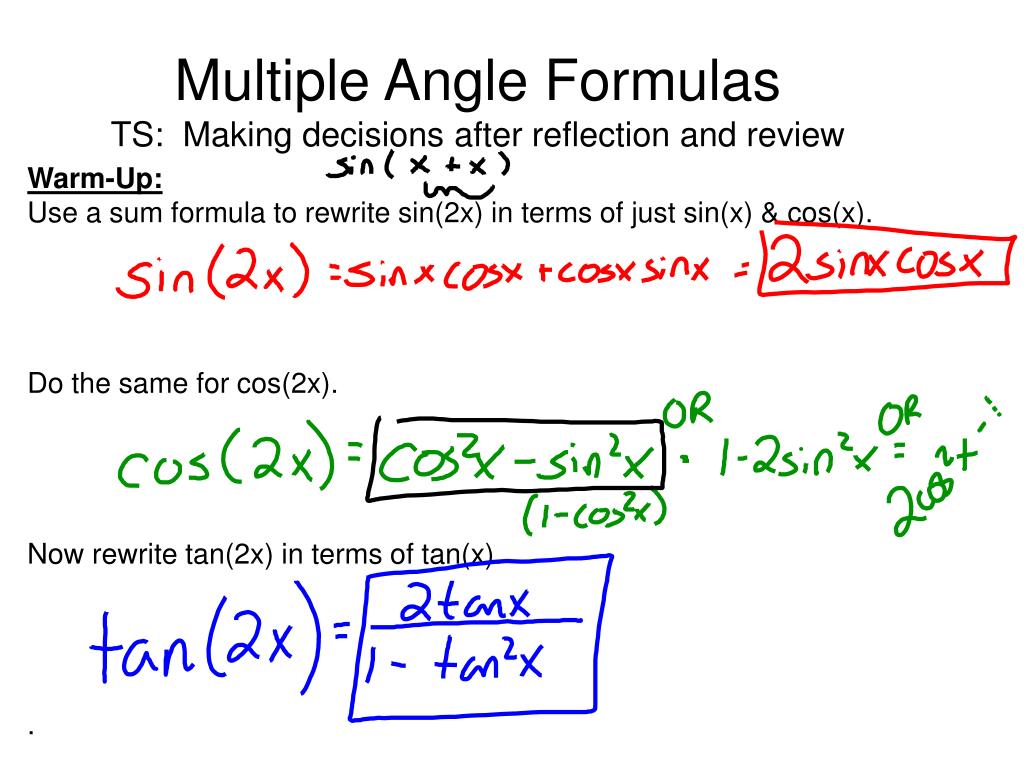
Multiple Angle Formulas Es Demonstrating Understanding Of Concepts Warm Up Use A Sum Formula To Rewrite Sin 2x In Terms Of Just Sin X Cos X Do Ppt Download


What Is The Identity Tan 2x Equal To In Terms Of Sinx And Cosx Quora


Integrate Rational Function Of Sine And Cosine T Tan X 2 Part 1 Youtube



Txt 02 Std 11 Mathematics By Saurabh Suman Issuu
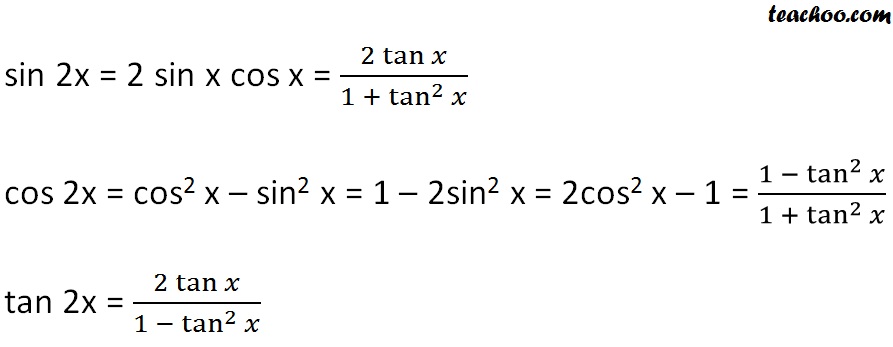


Double Angle Formulas Trigonometry Teachoo 2x 3x Formula Provi



Expressing Sin X And Cos X In Terms Of T Tan X 2 Youtube
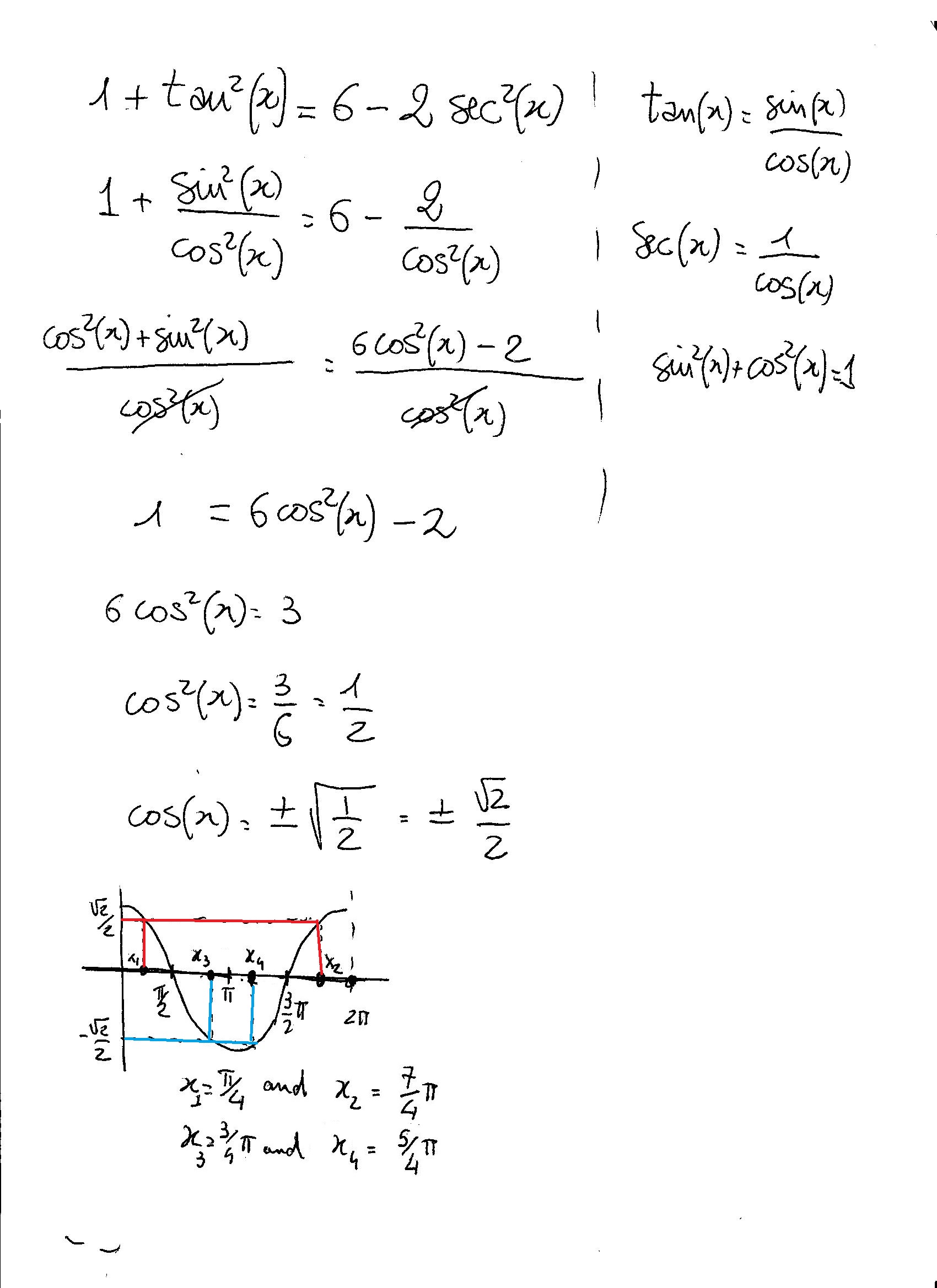


How Do You Solve 1 Tan 2x 6 2sec 2x Socratic



If Sin 4x Sin 2x 1 Then Prove That Tan 4x Tan 2x 1 Brainly In


Ppt Multiple Angle Formulas Ts Making Decisions After Reflection And Review Powerpoint Presentation Id



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿